Learning to Extract Context
for Context-Aware LLM Inference
for Context-Aware LLM Inference
- We propose ContextLens, a lightweight context generator that extracts user intent, ambiguity, and risk factors from prompts to enable safer LLM inference
- Our method reduces harmful responses by 5.6% on SafetyInstruct and improves safety-helpfulness balance by 6.2% on XSTest/WildJailbreak
- Context snippets are transferable across models and can improve both small (3B) and large (GPT-4) foundation models
- RL-based training with autoencoder-style objective ensures context remains grounded in the original prompt
We propose a context-aware inference framework that first generates a prompt-grounded context snippet capturing user intent, ambiguity, and potential risks, then conditions any LLM on this enriched input. A reinforcement-learned context generator is trained in an autoencoder-like setup to maximize safety and prompt reconstruction while discouraging trivial copying. This improves refusal accuracy on harmful prompts and preserves helpfulness on benign requests across multiple base models and safety benchmarks.
Disentangles context generation from response decoding to avoid co-adaptation of reasoning traces.
Reward combines prompt reconstruction and safety signals for the context.
Contexts generated by a 3B model improve any types of LLMs.
💡 The Problem: Current LLM Inference
Current LLMs face two critical failure modes in safety-critical applications:
- Over-refusal: Models trained to reject harmful prompts often collapse to refusing benign requests that contain words commonly found in harmful prompts (e.g., "destroy" or "kill")
- Adversarial vulnerability: Without understanding why a request is unsafe, models are susceptible to simple adversarial manipulations that bypass safeguards
Key Insight: User prompts are often ambiguous or under-specified. Subtle contextual cues—such as user intent, prior knowledge, and potential risks—strongly influence what constitutes an appropriate response. Existing models generate immediate responses without considering these broader contextual factors.
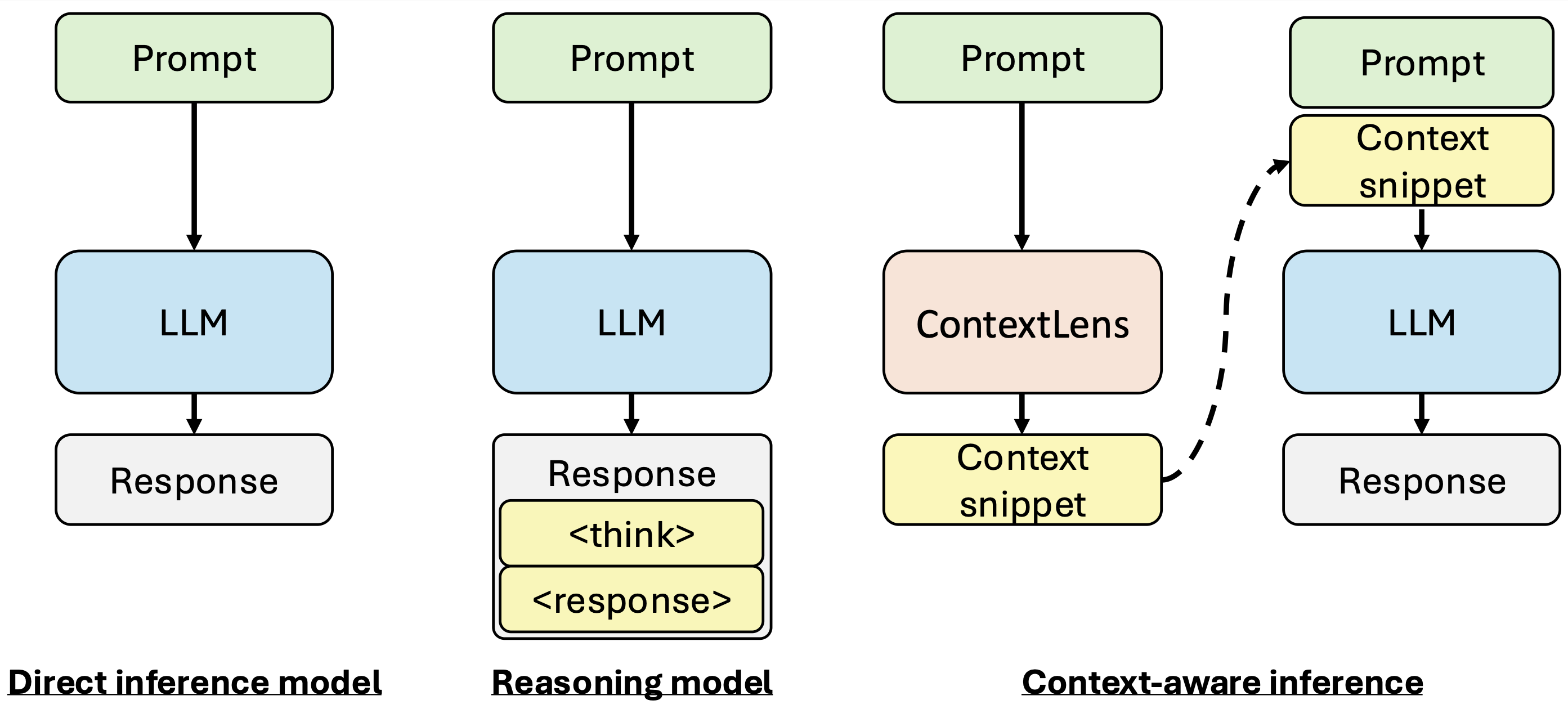
Figure 1: Comparison of inference paradigms. Traditional models (left) and reasoning models (middle) vs. our context-aware inference (right).
🚀 Our Approach: ContextLens Framework
We propose context-aware inference that disentangles the response model from a dedicated context generator (ContextLens). Our framework extracts contextual information from user prompts and uses it to guide safer response generation.
Key Components:
- Context Generator (gθ): A lightweight LLM (e.g., Qwen 3B) that produces context snippets describing user intent, ambiguity, and potential risks
- Decoder Model (d): A frozen external model (e.g., Llama 3B) used during training to ensure transferability
- Autoencoder Architecture: Context must retain enough information to reconstruct the original prompt, preventing collapse into simple answer generation
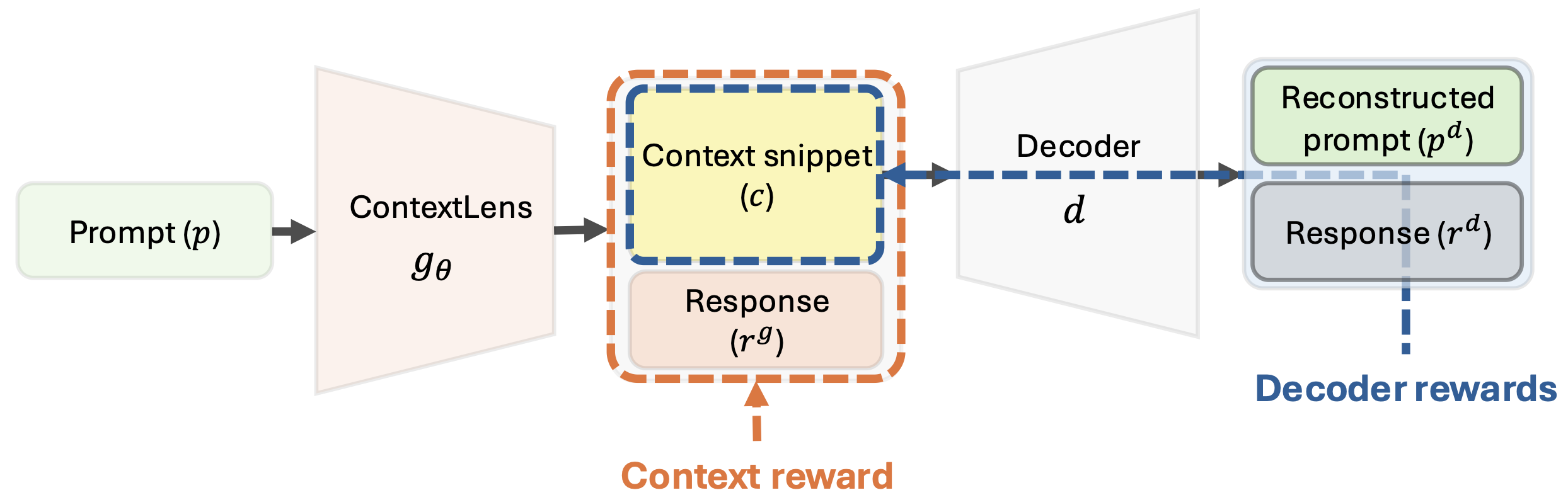
Figure 2: ContextLens training framework. The context generator produces context snippets that help a frozen decoder model reconstruct the prompt and generate safe responses.
Training Innovations:
- Cross-model Training: Context generator (gθ) is trained to benefit not only itself but also an external fixed decoder model (d), promoting transferability across models
- Autoencoder Loss: Decoder model reconstructs the original prompt from generated context + partially masked prompt, ensuring context remains grounded
- RL-based Optimization: Trained with GRPO (Generalized Reward Policy Optimization) using a composite reward:
- Prompt reconstruction similarity: SIM(pd, p)
- Safety of generator's response: Safe(rg)
- Safety of decoder's response: Safe(rd)
- Copy-prevention penalty to avoid trivial solutions
🧪 Three Approaches to Generate Context Snippet
We explore three methods for generating context snippets, from zero-shot prompting to full RL training:
1. Thinking Traces from Reasoning Models
Leverages intermediate reasoning steps from models trained with chain-of-thought reasoning on safety data. We extract thinking traces from:
- Supervised fine-tuned reasoning models (e.g., SafeChain)
- RL-trained reasoning models (e.g., TARS)
Limitation: Not explicitly optimized for transferability or prompt reconstruction
2. Zero-Shot Context Generator
Uses a fixed prompt template with off-the-shelf LLMs to elicit context without any training. The template instructs the model to output five sections:
- User Intent: Identifying the user's goal
- Ambiguity: Unclear aspects of the request
- Potential Risks: Enumerating safety concerns
- Action Decision: Direct answer, ask clarification, or refuse
- Safe Response Plan: Strategy for handling the request
Advantage: Annotation-free, requires only a single forward pass, provides baseline contextualization
3. ContextLens (RL-Trained Generator)
Our proposed method directly optimizes a lightweight context generator with GRPO to produce:
- Transferable context that works across different foundation models
- Grounded context that retains information about the original prompt
- High-quality safety signals without co-adaptation to specific models
Result: 3B model that produces context benefiting both small and large foundation models
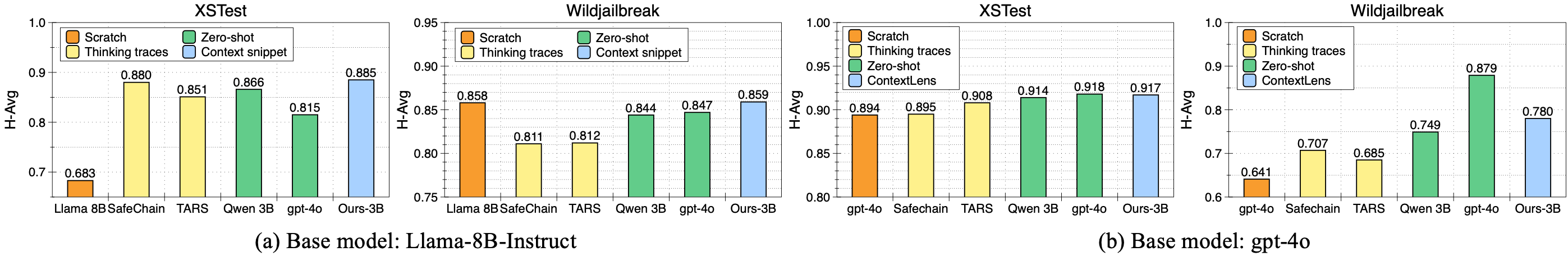
Figure 3: Comparison of different context generation approaches and their effectiveness on different base models.
📊 Main Results: Performance Across Models
ContextLens improves safety across multiple foundation models and benchmarks. We evaluate on:
- SafetyInstruct: Harmful prompt detection (lower ASR = better)
- XSTest & WildJailbreak: Balance between safety and helpfulness (higher harmonic mean = better)
Key Findings:
- 5.6% average reduction in harmful responses on SafetyInstruct (ASR metric)
- 6.2% improvement in harmonic mean on XSTest/WildJailbreak
- 4.21% gain on GPT-4 and 10.55% gain on Llama-8B with RL-trained ContextLens
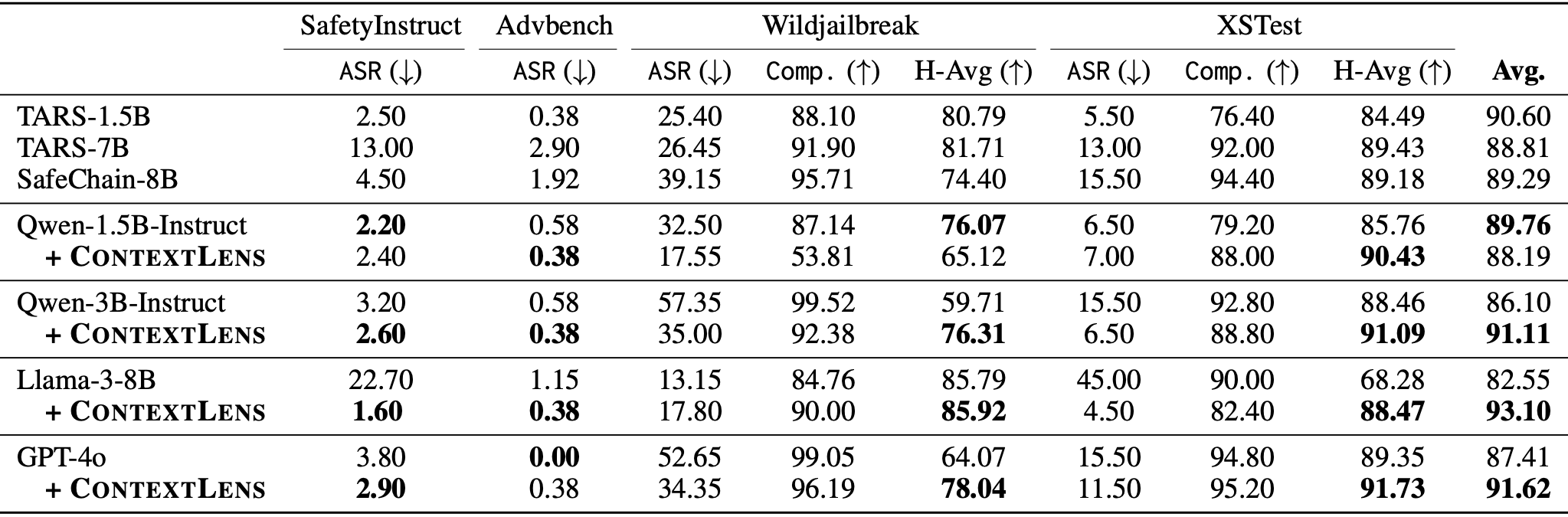
Table 1: Performance comparison across different base models (Qwen-1.5B, Qwen-3B, Llama-8B, GPT-4) with and without context snippets. Results show consistent improvements across all models and benchmarks.
Transferability Results:
- Context generated by a 3B model successfully improves much larger models (8B, GPT-4)
- RL-trained ContextLens shows best overall performance, demonstrating value of explicit context optimization
✨ Context Quality Analysis
We evaluate the quality of generated context snippets through multiple dimensions:
Quality Metrics:
- Coherence: Does the context remain faithful to the original prompt?
- Relevance: How much relevant information about intent and risks is captured?
- Overall Quality: Is overall quality of context snippets good?
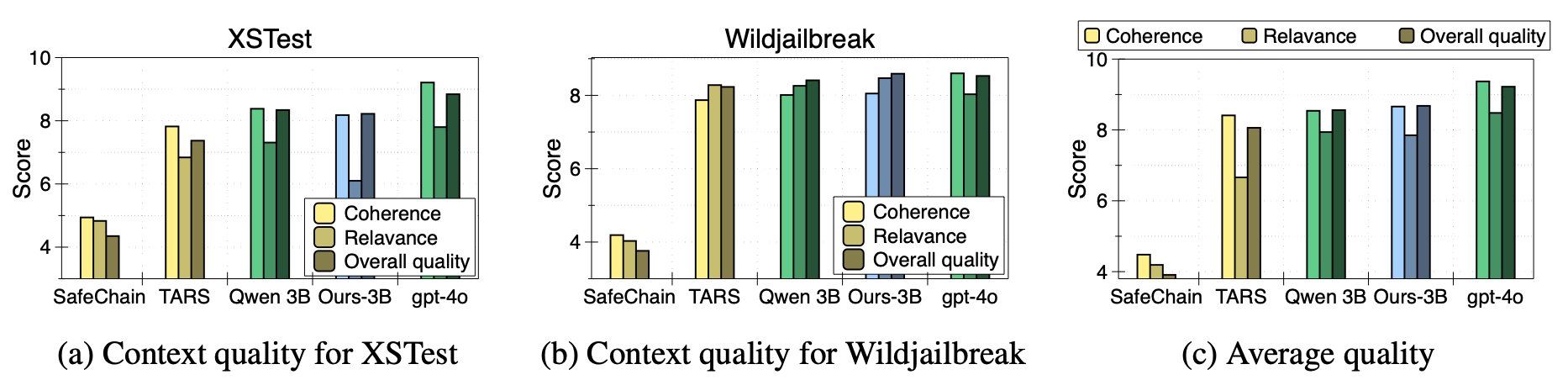
Figure 4: Context quality measured directly by LLM-as-a-Judge in three categories: Coherence, Relevance with prompt and context snippets, and overall quality of context snippets.
Quality Evaluation:
- Detection rate: How much context snippets help detection guard models to detect the harmfulness of the prompt?
- Monitorability: How much context snippets help to monitor the model’s predictive behavior?
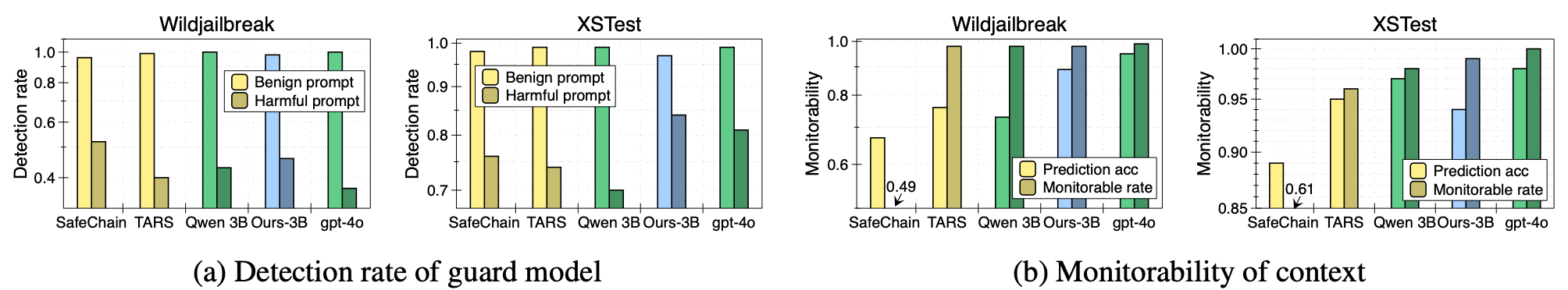
Figure 5: Evaluation of context informativeness. (a) Comparison of different context types on the prompt-detection task when the context snippet is given using the Llama-3-Guard-8B model. (b) Comparison of the monitorability of context snippets, assessing whether they contain information that can influence the model’s predictive behavior.